CNC Turning Services from China
China high-quality precision CNC turning services you can trust. Competitive pricing and fast lead times.
- Over 60 Certified Materials
- Custom Finishes
- ±0.005mm Tight Tolerance
- Lead times from 7 days
Save 30% on average!
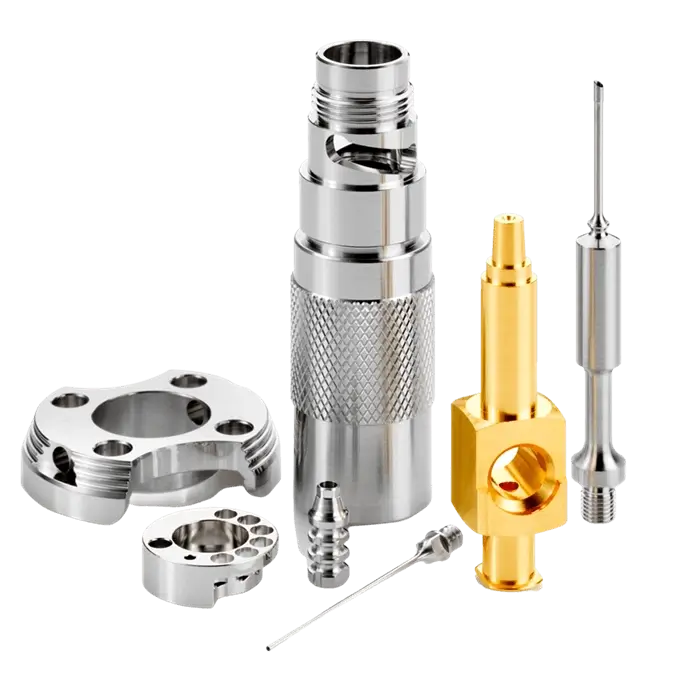

Vertex is a leading manufacturer of CNC-turned parts delivering excellent quality flexibly. Our highly skilled engineers, designers, and procurement teams ensure our services are provided on time and within budget.
Our state-of-the-art CNC turning centers & lathes, combined with various finishing options, make us the perfect choice for your precision manufacturing requirements, from prototyping to production runs.
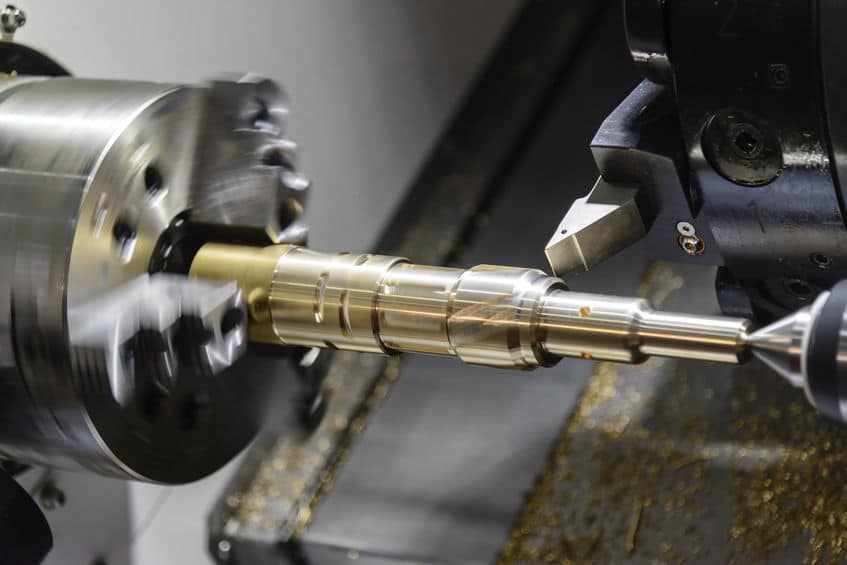




Rapid Turnaround
We’re committed to reducing friction at every stage, so you can be as delighted with the speed of your CNC Turned parts’ arrival as you are with their exceptional quality. Order now to receive your parts in as little as 5 days!
High Accuracy
Our standard CNC tolerance is +/- 0.127mm, and when you use our tolerance configurator, you can expect precision machining to be +/- 0.005mm.
A Wide Variety Of Materials
We offer over 60 production-grade materials including metal, plastic, and ceramic, and take great care to ensure the right material is used for every part.
Perfect Finish
We offer high-quality finishing processes for most CNC Turned parts; including anodizing, polishing and plating, heat treatment, powder coating, and more.
Part size limitations
Metric units
Imperial units
Maximum speed: 2000RPM
Motor power: 750W
From intricate medical and aerospace designs to complex industrial parts, our ISO 9001-certified company creates precision components with the highest level of accuracy. We utilize CNC turning lathes for complex machining projects requiring tight tolerance specifications up to ±0.005” – as close as a few thousandths of an inch! Our standards for metals follow ISO 2768-m while plastics adhere to requirements set by ISO 2768-c.
Type
Tolerance
+/- 0.025 mm
+/- 0.001 inch
+/- 0.025 mm
+/- 0.001 inch
+/- 0.025 mm
+/- 0.001 inch
950 * 550 * 480 mm
37.0 * 21.5 * 18.5 inch
Our CNC machining experts have carefully compiled the ideal characteristics for creating precision components. This table shows what works best, and also presents any technical limits to keep in mind during production.
Feature
Recommended Size
Feasible Size
Ø 2.5 mm
Ø 0.5 mm
R 8 mm
R 0.25 mm
0.8 mm (for metals)
1.5 mm (for plastics)
0.5 mm (for metals)
1.0 mm (for plastics)
Diameter:standard drill bit sizes
Depth: 4 x diameter
Diameter: Ø 0.5 mm
Depth: 10 x diameter
Size: M6 or larger
Length: 3 x diameter
Size: M2
Vertex offers a wide variety of materials for custom CNC machining, plastic, and metal, including but not limited to:
Aluminum: Aluminum’s strength-to-weight ratio, affordability, and recyclability have made it widely used across industries worldwide.
Alloys: 6061-T6, 7075-T6, 2024, 5052, 6060, 5083, 2017, 6082
Finishing Options: Alodine, Anodizing Types II, III, III + PTFE, ENP, Media Blasting, Nickel Plating, Powder Coating, Tumble Polishing

Stainless steel: Stainless steel’s corrosion resistance and ductility make it ideal for long-term exposure to elements and easy shaping into different forms
Finishing Options: As machined, Bead Blasted, Polishing, Decorative Chrome Plating, Powder Coat, Nickel Plating, Gold Plating, Silver Plating
Alloys: SS303, Stainless Steel 304/304L, Stainless Steel 316/316L, Stainless Steel 17-4, Stainless Steel 416, etc.

Alloy Steel: Alloy steel is steel mixed with elements like manganese, nickel, and chromium to enhance its strength, hardness, corrosion resistance, and durability, tailored to meet specific application needs.
Alloy: AISI 1215, AISI 4140, AISI 4340, AISI 8620, AISI 4130
Finishing Option: Polishing, Plating, Painting, Powder Coating and etc.

Tool Steel: Tool steel is a type of high-carbon and high-alloy steel that is specifically designed to be used in the manufacture of cutting tools, dies, and molds. It is valued for its high hardness, wear resistance, and toughness, which make it suitable for applications where the tool is subjected to repeated impacts or stresses.
Alloy: A2 Tool Steel, D2 Tool Steel, O1 Tool Steel, S7 Tool Steel, M2 Tool Steel
Finishing Option: Bead/Sand Blast, Polishing, Plating, Painting, Powder Coating, Heat Treatment and etc.

Brass: Brass is an alloy of copper and zinc, especially metal material with more than 20% zinc content, which is the most commonly used metal material in cnc machining
Finishing Options: Nickel Plating, Bead Blasted, Gold Plating, Silver Plating
Alloy: C360, C260

Copper: Copper is a soft, malleable metal with excellent thermal and electrical conductivity, making it an essential material in many industries.
Grade: C10100, C11000, C12200, C14500, C17200
Finishing Option: Plating, Polishing

Titanium:Titanium has a low density and high strength, making it ideal for applications that require a strong yet lightweight material, such as aerospace, automotive, and biomedical industries. It is also highly resistant to corrosion and can withstand exposure to many chemicals and environments
Alloy: Ti-6Al-4V, Ti-6Al-2Sn-4Zr-2Mo, Ti-3Al-2.5V
Finishing Option: Polishing, Anodizing, Sandblasting, Chemical etching, Laser engraving and etc.

Magnesium: Magnesium is a versatile and lightweight metal with a silvery-white appearance, known for its exceptional strength-to-weight ratio, excellent thermal and electrical conductivity, and widespread use in industries such as aerospace, automotive, and healthcare.
Alloy: AZ31B, AZ91D, We43, AM60B, ZK60A, QE22
Finishing Option: Blasting, Anodizing, Chromate Conversion Coating, Passivation, Powder Coating, Electroplating etc.
POM (Delrin/Acetal): High stiffness, good moisture resistance, high wear-resistance, and low friction, easy to machine
Color: White, black, brown
Grade: POM-C, POM-H, UV stabilized POM, Food-Grade POM

PMMA: PMMA is commonly known by the trade name “acrylic” or “plexiglass”. It is a lightweight and shatter-resistant material that is often used as a glass substitute in applications such as skylights, displays, signage, and lenses
Color: Transparency
Grade: Extruded PMMA, Cast PMMA, Impact-Modified PMMA, UV-Stabilized PMMA, Heat-Resistant PMMA

PEEK: PEEK is a high-performance engineering thermoplastic with excellent mechanical, chemical, and thermal properties, short for Polyether Ether Ketone
Color: Beige with no transparency
Grade: Unfilled PEEK, 30% glass-fiber reinforced PEEK, 30% carbon-fiber-reinforced PEEK, Bearing Grade PEEK

ABS: ABS is tough, rigid, and lightweight, making it an excellent material for use in applications such as automotive parts, toys, electronic housings, and consumer goods. It is also resistant to impact, chemicals, and heat, making it a popular choice for use in harsh environments
Color: ABS is naturally opaque and comes in a range of colors including black, white, and gray
Grade: General purpose ABS, Flame retardant ABS, High impact ABS, Heat-resistant ABS

Nylon: Nylon is a strong, durable, and elastic material that is commonly used in textiles like clothing and ropes. Its resistance to abrasion, chemicals, and moisture makes it popular for industrial applications, such as gears, bearings, and automotive components
Color: Nylon is often used in its natural off-white or slightly yellowish color
Grade: Nylon 6, Nylon 6/6, Nylon 11, Nylon 12

PTFE: PTFE(Teflon) is a high-performance plastic material known for its exceptional chemical resistance, low friction coefficient, and high-temperature resistance
Color: The color of PTFE is typically white or off-white

PVC: PVC stands for polyvinyl chloride, which is a synthetic thermoplastic polymer that is widely used in various applications. PVC is a versatile material that can be rigid or flexible
Color: clear or opaque
Grade: UPVC, PPVC, CPVC

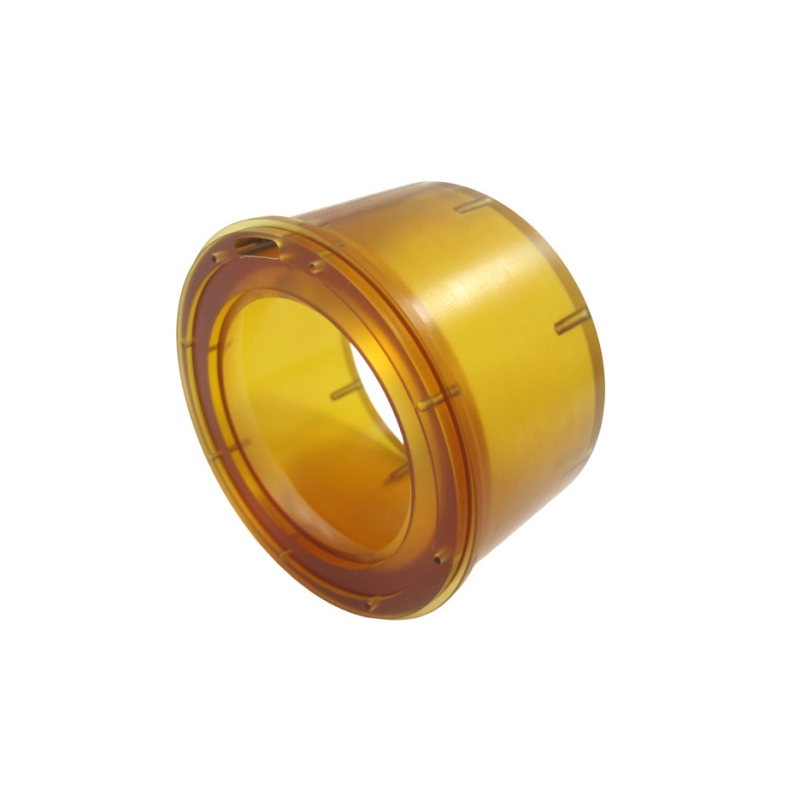
PEI: PEI has excellent mechanical, thermal, and electrical properties, as well as good chemical resistance
Color: Amber or brownish color
Grade: Unfilled PEI, Glass-Filled PEI, Carbon-Filled PEI, Ultem PEI

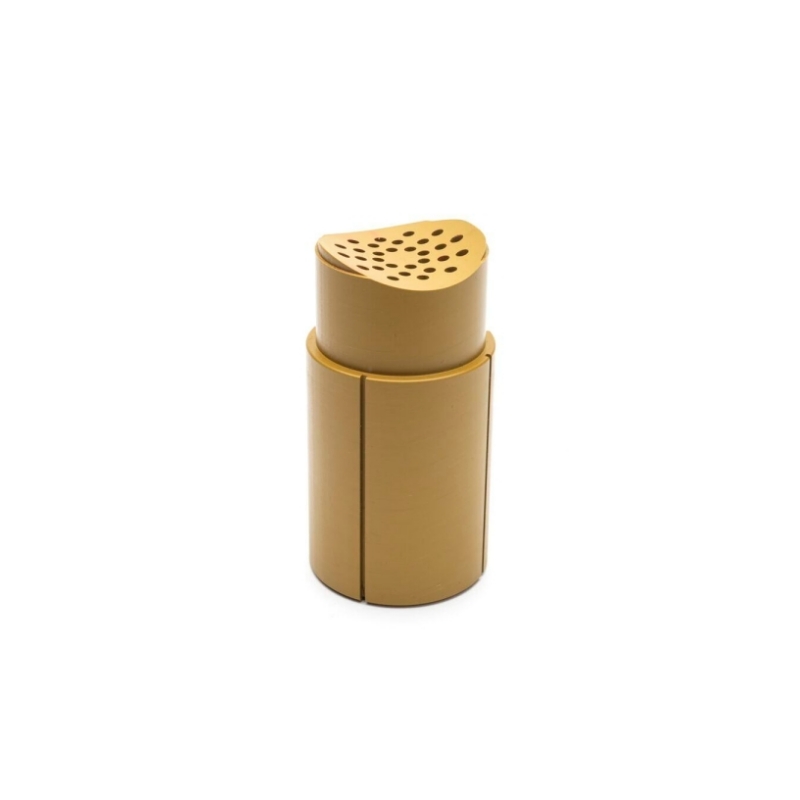
PAI: or Torlon Polyamide-imide, is a type of thermoplastic polymer that is known for its excellent mechanical properties that it maintains over a wide range of temperatures.
Color: Yellow
Grade: Torlon4203, Torlon4503, Torlon4301,Torlon4501

We machine rapid prototypes and low & large volume production orders for customers in multiple industries: medical devices, aerospace, automotive, defense, electronics, hardware startups, industrial automation, machinery, marine and robotics, and many more.
Applications Of CNC Turning
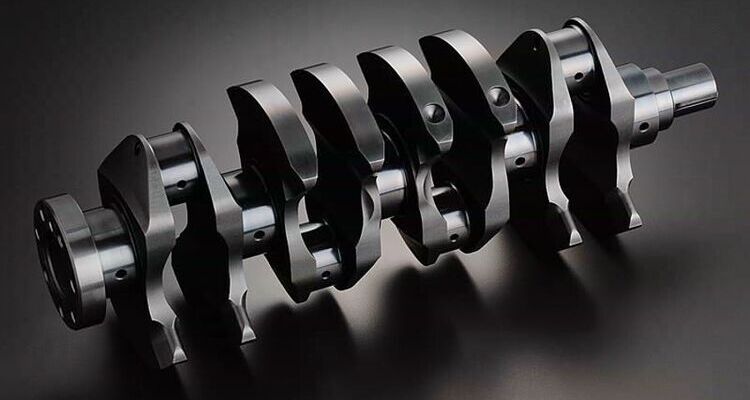

CNC turning is commonly used in the automotive industry to produce precision cylindrical components such as engine crankshafts, drive shafts, and brake rotors.
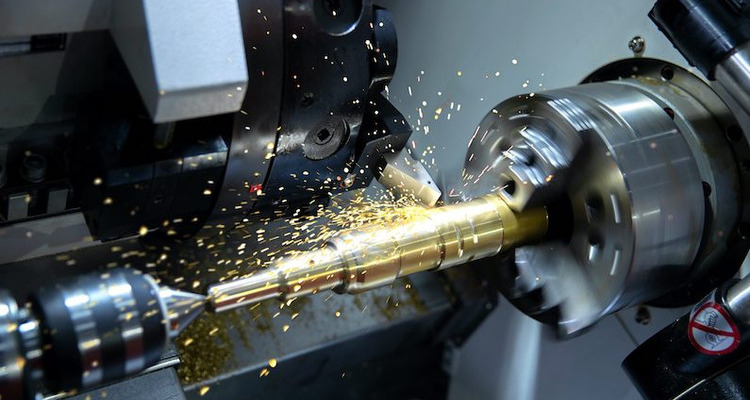

With its vast material range, low unit cost, and swift production capabilities, CNC stands out as an excellent alternative for rapid prototyping.
CNC turning is an essential process in the aerospace industry for manufacturing precision cylindrical components like turbine parts, hydraulic components, and landing gear shafts.
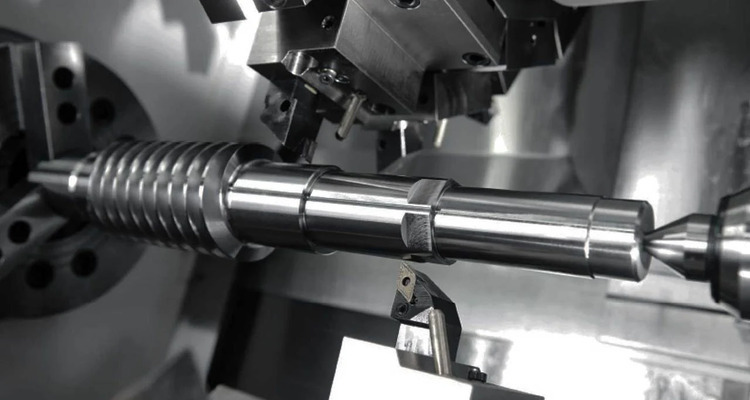

CNC turning is used in the industrial machinery sector to produce high-precision cylindrical components such as gears, couplings, and shafts.
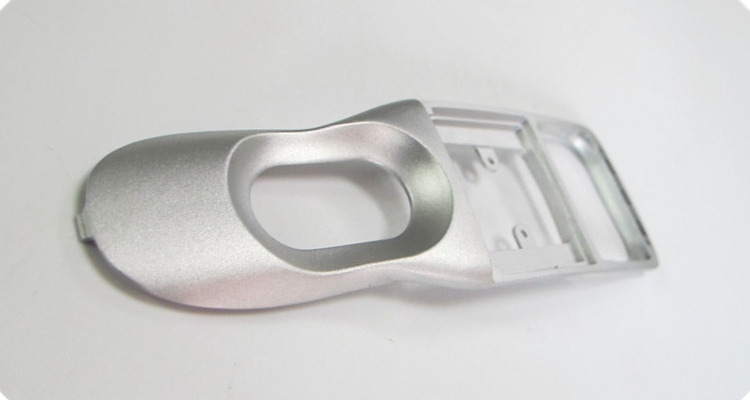

CNC turning is utilized in the medical device industry to create precision cylindrical components for various medical devices like surgical instruments, implants, and prosthetics.
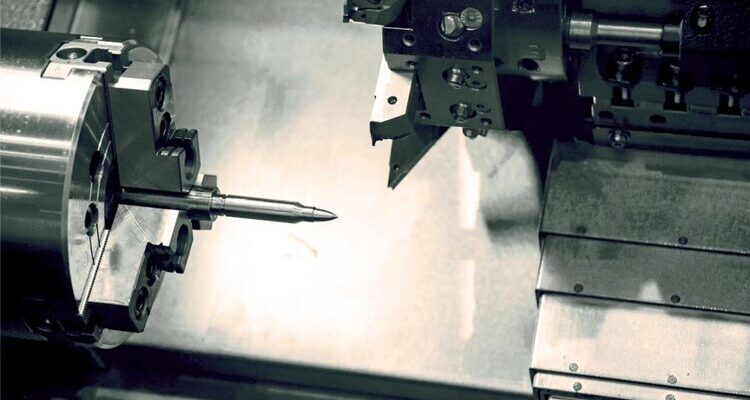

CNC Turning is widely used in the defense industry to create highly accurate and cylindrical components like artillery shells, gun barrels, and missile casings.
What is the difference between CNC milling and CNC turning?
CNC milling and CNC turning are two distinct machining processes that differ in how they operate, the types of machines used, and the parts they can produce.
CNC milling uses a rotating cutting tool that moves across a stationary workpiece to remove material from its surface. The milling process can produce a wide range of geometries, including flat and inclined surfaces, slots, and grooves.
CNC turning, on the other hand, rotates the workpiece while the cutting tool remains stationary, shaping the material into the desired shape. It is typically used to produce cylindrical parts and is ideal for creating symmetrical components like shafts, pins, and bushings.
In summary, CNC milling is ideal for producing parts with complex shapes and geometries, while CNC turning is perfect for creating cylindrical parts. Both processes provide high levels of precision, consistency, and efficiency while reducing the need for manual labor.
Is CNC lathe and CNC turning same?
CNC lathes and turning centers are not just two names for the same machine – they actually perform different tasks! Lathes generally rotate a part to create circular shapes, but with more advanced features like facing, threading, knurling drilling and reaming as well as taper turning capabilities; Turning Centers can help you produce even more intricate pieces.
What are the disadvantages of CNC turning?
- Only Rotatable Components Are Permitted
- Parts May Need Many Procedures and Machines
- Severe tool wear
- The processing produces a lot of Scrap
What is the difference between rough turning and finish turning?
Rough turning and finish turning are the two stages of the turning process used to make machined parts. Here are the primary differences between them:
- Cutting Depths: Rough turning removes large amounts of material quickly to achieve a particular shape with a relatively heavy cut depth. Finish turning uses smaller cutting depths to provide an improved surface finish and highly accurate dimensions.
- Speed: Rough turning is commonly done at higher speeds to remove material quickly, while finish turning is performed at lower speeds to provide a smoother surface finish and more precise cuts.
- Tool Selection: Because rough turning demands a heavier cut, it frequently employs larger and more robust tool inserts. Finish turning, on the other hand, generally utilizes smaller and lighter inserts for improved surface finishes.
- Cutting Path: Rough turning typically employs a straight cutting path, while finish turning may use a technique known as “light cuts,” which involves the tool following a slightly curved path.
Both stages are essential in the turning process, with rough turning used to remove bulk material and produce the desired shape, and finish turning used to refine the size and surface finish of the machined part.
What parts can be made with CNC turning?r service
Through the power of CNC turning, a multitude of parts necessary for production in a variety of industries can be crafted – from automotive components and aeronautical components to medical equipment pieces and toy parts. From hubs to flywheels, this technology is an invaluable tool that continues — day after day — powering countless essential items we use daily.
What are the benefits of CNC turning?
Higher Precision: CNC turning offers significantly higher precision than manual turning, allowing for extremely accurate machine parts.
Greater Efficiency: CNC lathes can complete multiple operations in a single setup, reducing the time and cost involved in producing machined parts.
Versatile Applications: CNC turning can be applied to an extensive range of materials, from metals to plastics, allowing for a diverse range of applications.
Consistent Quality: CNC turning ensures that every machined part is identical in design and output, guaranteeing consistent quality throughout production.
Lower Costs: With its high efficiency, automated operation, and consistent quality, CNC turning offers lower manufacturing costs in the long run, as compared to traditional methods.
